All About Calcium: Importance, Benefits, and Sources
Calcium Deficiency, Importance and Benefits.
Calcium is one of the most important minerals for the human body. Essential for bone health, it plays a crucial role in various biological functions. In this article, we dive deep into the importance of calcium, its benefits for the body, the best dietary sources, and tips to ensure adequate intake.
The Importance of Calcium in Human Health
Calcium is indispensable for survival. From childhood to adulthood, it actively contributes to the development of strong bones, healthy teeth, and the functioning of muscles and nerves. Its deficiency can lead to serious health issues such as osteoporosis and fractures.
Benefits of Calcium
Calcium offers multiple benefits to the body. Let’s explore the main ones:
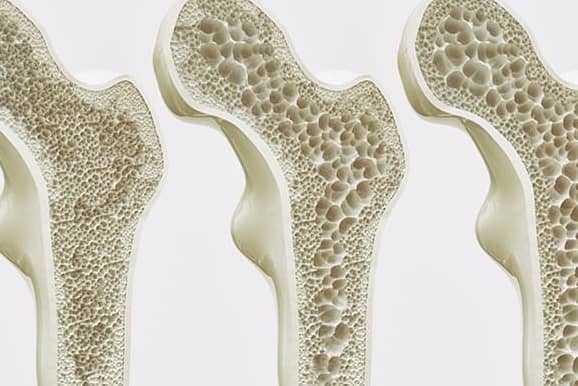
Bone Health and Osteoporosis Prevention
About 99% of the body’s calcium is stored in the bones and teeth. This mineral strengthens bone structure and helps prevent diseases like osteoporosis, a condition characterized by fragile bones.
Muscle and Nerve Function
Calcium is essential for muscle contraction, including heart function. It also plays a role in cell-to-cell communication by facilitating nerve impulse transmission.
Blood Clotting Regulation
Another crucial function of calcium is its role in blood clotting. This process is vital to prevent prolonged bleeding in case of injuries.
Metabolism and Hormonal Control
Calcium influences the functioning of various enzymes and is involved in the release of hormones, such as insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels.
Sources of Calcium in the Diet
While calcium is widely available in foods, choosing the right sources is essential to ensure effective absorption.
Dairy Products
Dairy products are the primary source of calcium in most diets. These include:
- Milk
- Cheeses (such as Parmesan and Cheddar)
- Natural or fortified yogurts

Leafy Green Vegetables
Leafy green vegetables are an excellent option for those seeking plant-based calcium. Examples:
- Spinach
- Kale
- Broccoli
Fortified Foods
Some foods are fortified with calcium to meet daily requirements, such as:
- Plant-based milks (almond, soy, oat)
- Breakfast cereals
- Orange juice
Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, chia seeds, and sesame seeds are rich in calcium and provide other important nutrients.
Fish with Bones
Fish such as sardines and canned salmon contain calcium in their bones, making them a good alternative to dairy.
Factors That Influence Calcium Absorption
Consuming calcium isn’t enough; the body needs to absorb it effectively. Some factors can improve or hinder this process.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption. Without it, the body cannot utilize calcium effectively. Sun exposure and foods such as eggs and fatty fish are good sources of vitamin D.
Excess Caffeine and Sodium
High levels of caffeine and salt in the diet can increase calcium excretion through urine, hindering its retention in the body.
Oxalates and Fiber Intake
Foods high in oxalates (like spinach) and fiber can reduce calcium absorption. While healthy, they should be consumed in moderation.
Daily Calcium Requirements
The amount of calcium needed varies depending on age, gender, and health status.
| Age Group | Daily Requirement (mg) |
|---|---|
| Infants (0-6 months) | 200 |
| Children (1-3 years) | 700 |
| Adults (19-50 years) | 1000 |
| Women > 50 years | 1200 |
Calcium Deficiency: Symptoms and Risks
Calcium deficiency, known as hypocalcemia, can cause:
- Muscle cramps
- Bone fragility
- Weak nails
- Increased risk of fractures
In the long term, calcium deficiency may lead to problems such as hypertension and irregular heart rhythms.
Calcium Deficiency and Its Impact on Teeth
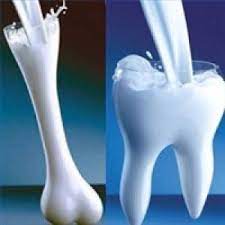
Calcium is a nutrient packed with benefits for both teeth and bones.
Calcium deficiency can have adverse effects on an individual’s dental health.
What Is the Relationship Between Calcium and Teeth?
Calcium is an essential nutrient that we need to consume to ensure strong bones and teeth.
When a person does not consume enough calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D, they may develop weaker, less dense bones and teeth.
This can lead to osteoporosis and other health complications, such as cavities and tooth loss.
Women with osteoporosis tend to have more dental problems than those of the same age without the condition. Osteoporosis sufferers often experience weakening or thinning of the jawbone. The consequence is a loss of adequate support for the teeth, resulting in tooth loss.
Calcium Deficiency – Symptoms
Calcium deficiency can cause bones throughout the body to become less dense and more fragile. When this occurs, an individual may become more susceptible to tooth loss.
According to an older study, researchers found a direct correlation between insufficient calcium intake and tooth loss.
The researchers observed that people who did not consume enough calcium daily were significantly more likely to lose at least one tooth over a two-year follow-up period.
Calcium Deficiency – Other Symptoms
Signs of calcium deficiency may not become apparent for several years because the human body compensates for dietary shortages by drawing calcium from the bones.
In the long term, calcium deficiency can cause:
- Low bone mass, also known as osteopenia;
- Increased risk of osteoporosis;
- Higher risk of bone fractures.
In severe cases of calcium deficiency, the following may occur:
- Seizures;
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers;
- Cardiac arrhythmias.
Prevention
Steps can be taken to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent calcium deficiency and its symptoms before they manifest.
Calcium Supplements: When Are They Necessary?
In some cases, calcium supplementation may be recommended, especially for:
- Older adults at higher risk of osteoporosis
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- People with lactose intolerance
Choosing the Right Supplement
Calcium supplements come in different forms, such as calcium carbonate and calcium citrate. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation.
Conclusion
Calcium is a vital nutrient for maintaining strong bones, healthy muscles, and various biological functions. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D sources is essential for optimal health. Adopting healthy habits, such as limiting caffeine and sodium intake, also contributes to calcium retention.
Whether through food or supplements, adequate calcium intake should be a priority at every stage of life. By taking care of your calcium levels, you are investing in a healthier life free from bone and metabolic issues.
All About Calcium: Importance, Benefits, and Sources – Search more: https://www.dentalis.com.br/blog/a-deficiencia-de-calcio-e-o-impacto-sobre-os-dentes/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-Consumer/
Healthy Chia Pudding with Fruits: A Delicious and Nutritious Treat



